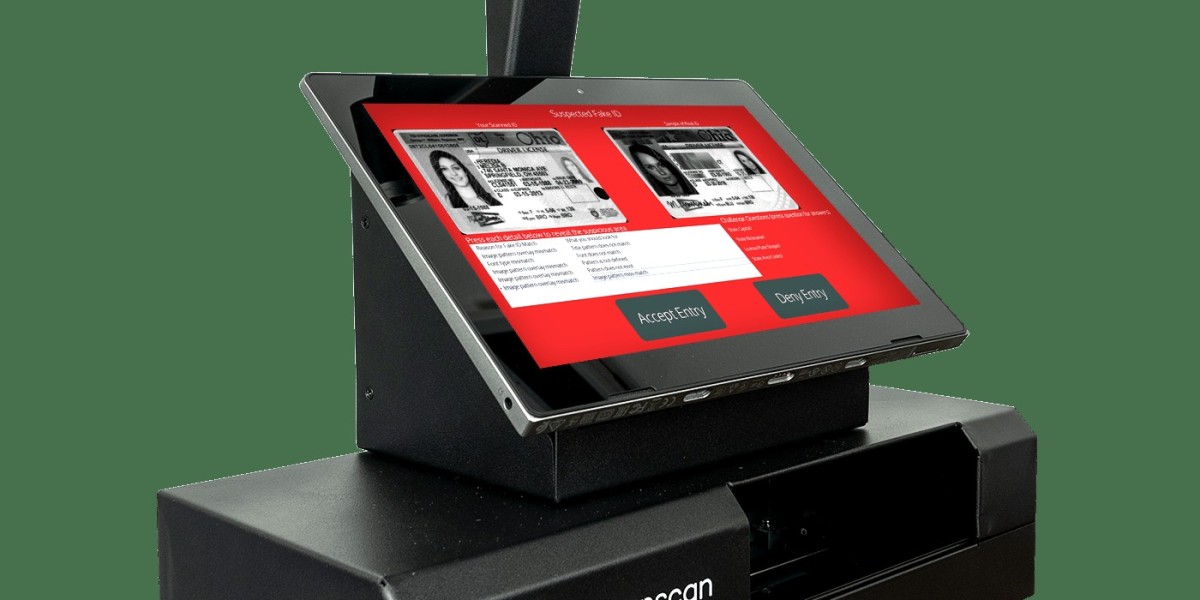
Id Scanner have become integral tools in various industries, offering a range of applications that enhance security and efficiency. These devices are equipped with advanced technologies that enable them to quickly and accurately capture and verify the information on identification documents, such as driver's licenses, passports, and ID cards. Below, we explore the primary applications and key technologies behind modern Id Scanner.
Applications of ID Scanners:
Age Verification: One of the most common uses of ID scanners is age verification, particularly in businesses like bars, clubs, and liquor stores. These scanners quickly confirm a person's age by scanning and validating the date of birth on their ID, helping businesses comply with legal age restrictions.
Access Control: ID scanners are used for access control in various settings, including offices, government buildings, and secure facilities. By scanning IDs or badges, they grant or deny access to authorized individuals, enhancing security.
Visitor Management: In corporate and educational environments, ID scanners are used for visitor management. They record visitor information, issue temporary access passes, and help monitor and control the flow of visitors.
Event Ticketing: At concerts, sporting events, and conferences, ID scanners are employed for ticket validation and fraud prevention. They ensure that tickets are not duplicated or used fraudulently.
Identity Verification: In financial institutions and during online transactions, ID scanners are used to verify the identity of customers. This is crucial for preventing fraud and complying with Know Your Customer (KYC) regulations.
Data Capture: Many organizations use ID scanners to digitize identification documents, extracting and storing data in electronic databases for various purposes, including record-keeping and analysis.
Key Technologies in Modern ID Scanners:
Optical Character Recognition (OCR): OCR technology is essential for reading and extracting text from identification documents. It allows scanners to capture and interpret the information on IDs accurately.
Barcode and RFID Scanning: Some IDs, like driver's licenses, may contain barcodes or RFID chips that store additional information. Modern ID scanners can read and decode these codes for enhanced verification.
Biometric Integration: Some advanced ID scanners incorporate biometric technologies such as fingerprint or facial recognition to enhance security and ensure that the person presenting the ID matches the data on the document.
Database Integration: ID scanners often connect to databases containing information about lost or stolen IDs. This helps organizations quickly identify fraudulent or compromised documents.
Mobile Applications: Many ID scanners are now available as mobile apps, allowing users to scan IDs using smartphones or tablets. This flexibility is especially valuable for businesses that require ID verification on the go.
Cloud Connectivity: ID scanners with cloud connectivity can instantly cross-reference scanned data with online databases for real-time verification and updates.
In conclusion:
Modern Id Scanner are versatile tools with diverse applications across various industries. They rely on technologies like OCR, barcode scanning, and biometrics to enhance security, streamline processes, and ensure accurate identification. As technology continues to advance, ID scanners are likely to play an increasingly crucial role in safeguarding information and enhancing efficiency in an ever-evolving world.
For more information visit IDPAPA