In the world of medicine, the term "angiotensin II receptor blocker" may sound complex, but it plays a vital role in managing various health conditions. In this article, we will unravel the mysteries surrounding angiotensin II receptor blockers, often abbreviated as ARBs. Whether you're a healthcare professional or someone seeking insights into this medication, we've got you covered.
Angiotensin II receptor blockers, or ARBs, are a class of medications that have gained prominence in the field of medicine. They are known for their effectiveness in managing several health conditions, particularly those related to cardiovascular health. In this article, we will explore the mechanisms behind ARBs, their applications, potential side effects, and much more.
What Is Angiotensin II?
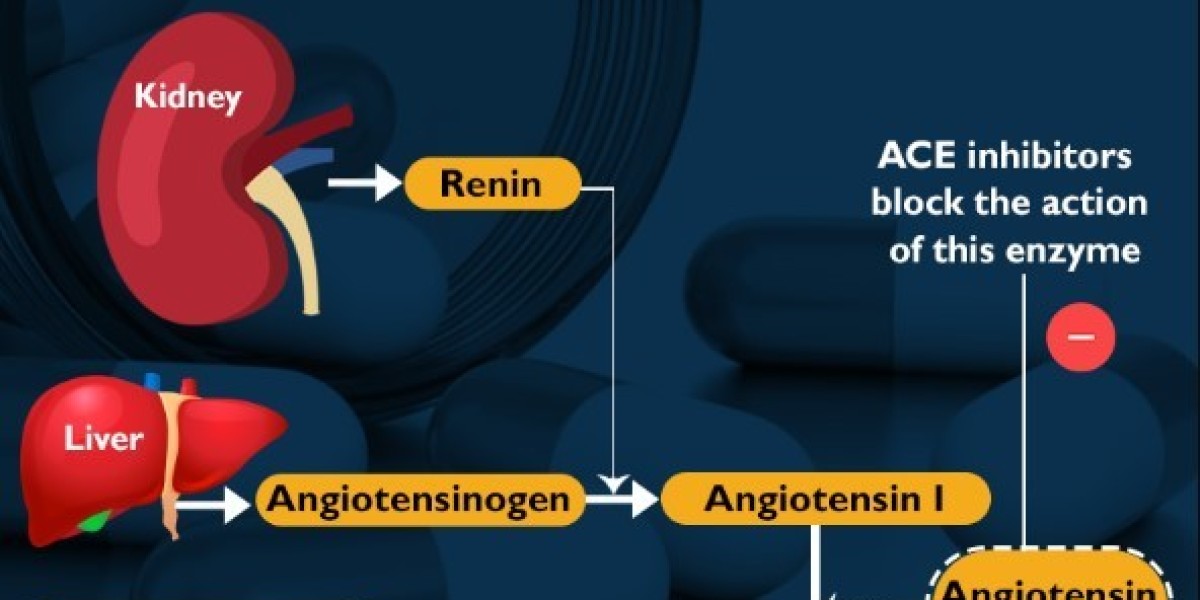
To understand ARBs, we must first grasp the concept of angiotensin II. Angiotensin II is a hormone naturally produced by the body. It plays a pivotal role in regulating blood pressure and fluid balance. Its functions are tightly controlled by the body to ensure overall health and well-being.
The Role of Angiotensin II in the Body
Angiotensin II acts on blood vessels, causing them to constrict or narrow. This constriction increases blood pressure, which is essential in situations where the body needs an immediate response, such as during times of stress or injury. However, when angiotensin II levels are chronically elevated, it can lead to health issues like hypertension.
Why Are Angiotensin II Receptor Blockers Used?
Angiotensin II receptor blockers, as the name suggests, block the action of angiotensin II. They do this by binding to specific receptors on blood vessels, preventing angiotensin II from exerting its vasoconstrictive effects. This action is beneficial in various medical conditions, particularly those related to hypertension and heart health.
How Do ARBs Work?
ARBs work by selectively blocking the angiotensin II receptors in the body. This prevents angiotensin II from binding to these receptors and exerting its effects. As a result, blood vessels remain relaxed, leading to lowered blood pressure. ARBs are often prescribed to help manage hypertension, heart failure, and other cardiovascular conditions.
Commonly Prescribed ARBs
Several ARBs are available in the market, each with its unique characteristics. Some of the commonly prescribed ARBs include losartan, valsartan, irbesartan, and candesartan. These medications offer choices for healthcare professionals to tailor treatment plans to individual patient needs.
Conditions Treated with ARBs
ARBs are versatile medications used to manage a range of health conditions, including:
- Hypertension (high blood pressure)
- Heart failure
- Diabetic nephropathy (kidney disease associated with diabetes)
- Prevention of stroke and cardiovascular events in high-risk individuals
Dosage and Administration
The dosage of ARBs can vary depending on the specific medication and the patient's condition. Healthcare providers carefully evaluate each patient to determine the appropriate dosage and administration schedule. It's crucial to follow the prescribed regimen to achieve optimal results.
Benefits of ARBs
Angiotensin II receptor blockers offer several benefits, including:
- Effective blood pressure control
- Reduced strain on the heart
- Protection against certain cardiovascular events
- Improved kidney function in some cases
Potential Side Effects
Like any medication, ARBs can have side effects. Common side effects may include dizziness, fatigue, and headache. It's essential to discuss any concerns with your healthcare provider to manage these side effects effectively.
Precautions and Interactions
Patients taking ARBs should be aware of potential drug interactions and precautions. It's vital to inform your healthcare provider about any other medications or supplements you are taking to avoid adverse effects.
Choosing Between ARBs and ACE Inhibitors
Healthcare providers often weigh the benefits and risks of ARBs against ACE inhibitors, another class of medications used for similar conditions. Understanding the differences between these two options is crucial for informed decision-making.
ARBs and Hypertension
Hypertension is a widespread condition that can have serious health consequences. ARBs are frequently prescribed to help lower blood pressure and reduce the risk of associated complications.
Future Developments in ARB Research
Ongoing research continues to explore the potential benefits and applications of ARBs. Future developments may uncover new uses for these medications and further improve their effectiveness.
Conclusion
In conclusion, angiotensin II receptor blockers (ARBs) are valuable medications with a broad range of applications in managing various health conditions, particularly those related to cardiovascular health. Understanding how ARBs work and their potential benefits can empower individuals to make informed decisions about their health.