The antimony market is witnessing dynamic shifts, driven by increasing demand from industries such as flame retardants, electronics, batteries, and automotive components. Antimony, a critical metalloid, is extensively used in alloys and semiconductors, highlighting its strategic significance in modern manufacturing. Over the past decade, global production and consumption patterns have evolved significantly due to technological advancements, regulatory changes, and fluctuating raw material availability.
Key Market Drivers
One of the primary growth drivers of the antimony market is its widespread application in flame retardants. Antimony trioxide is a preferred additive in plastics, textiles, and coatings, enhancing fire safety standards. The surge in electronics manufacturing, particularly in semiconductors and lead-acid batteries, has further fueled demand. Additionally, government regulations emphasizing safety and fire-resistant materials in construction and automotive sectors are contributing to market expansion.
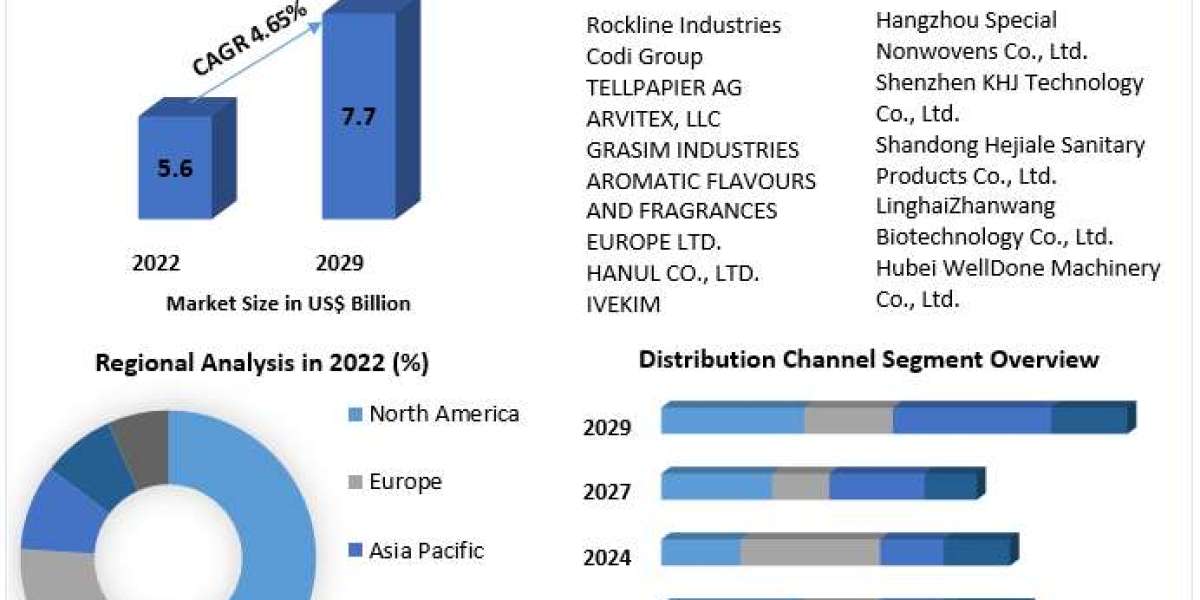
Economic development in emerging regions, especially Asia-Pacific, has bolstered industrial activities, leading to higher antimony consumption. China, being the largest producer, continues to dominate global supply, while countries like Russia and Bolivia contribute significantly to international trade. The market benefits from steady industrial demand coupled with innovations in material sciences, which are increasing the adoption of antimony-based products in newer applications.
Regional Insights
Asia-Pacific remains the largest antimony-consuming region due to robust industrialization, particularly in China, India, and South Korea. The electronics and automotive industries in these countries are key end-users. North America and Europe also exhibit steady demand, driven by regulatory compliance for fire safety and growing electric vehicle production. Latin America and the Middle East are emerging markets, presenting opportunities for mining investments and export-driven trade.
Market Challenges
Despite promising growth, the antimony market faces certain challenges. Resource scarcity and concentrated production in a few countries expose the supply chain to geopolitical risks and price volatility. Environmental concerns related to mining and processing, including waste disposal and emissions, require stringent regulations, potentially increasing production costs. Moreover, alternative materials and technologies for flame retardants and batteries pose a threat to traditional antimony applications, demanding innovation to maintain competitiveness.
Competitive Landscape
The global antimony market is moderately consolidated, with key players focusing on capacity expansion, technological upgrades, and strategic partnerships. Companies are investing in research to enhance product efficiency, explore new applications, and comply with environmental norms. Strategic collaborations with end-use industries, particularly in electronics and automotive sectors, are strengthening supply chain reliability and ensuring long-term contracts.
Additionally, mergers and acquisitions are shaping market dynamics by enabling companies to diversify geographically and expand production capacities. Players are also exploring recycling initiatives to reduce dependency on primary mining, thereby minimizing environmental impact and optimizing cost efficiency.
Future Outlook
The antimony market is projected to grow steadily over the next decade, driven by rising industrialization, technological adoption, and regulatory emphasis on fire safety. Demand for antimony in lithium-ion batteries is expected to increase as electric vehicle penetration accelerates globally. Moreover, ongoing research in antimony alloys and semiconductors could unlock new industrial applications, enhancing the market’s growth trajectory.
Sustainability trends are likely to influence market strategies, with manufacturers prioritizing eco-friendly processing methods and resource-efficient production techniques. Regions with untapped reserves may attract investments, ensuring diversification of supply and minimizing geopolitical risks. Overall, stakeholders can anticipate a balanced growth pattern, with emerging applications complementing traditional uses, positioning the antimony market as a critical component in future industrial development.
Conclusion
In summary, the antimony market is poised for significant growth due to its diverse applications, technological relevance, and increasing industrial adoption. While challenges like supply concentration and environmental regulations persist, innovations and strategic expansions are strengthening market resilience. For investors, manufacturers, and policymakers, understanding the evolving dynamics of the antimony market is essential for making informed decisions and capitalizing on emerging opportunities.