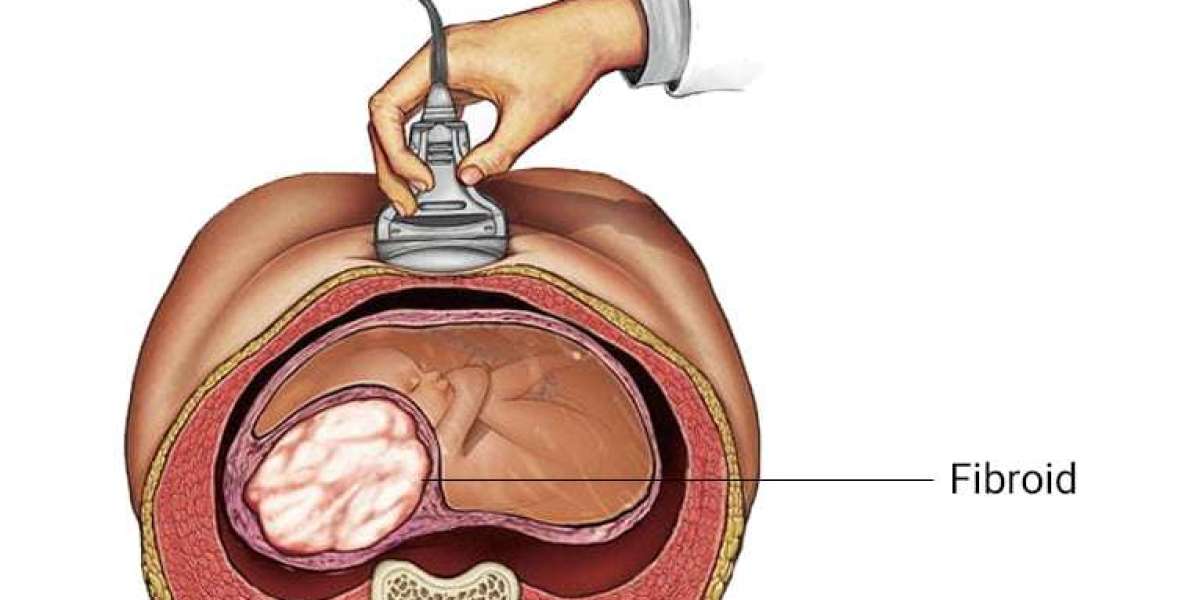
The uterine fibroid treatment market, catering to women with benign tumors affecting the uterus, has grown due to technological advancements, rising awareness, and increasing prevalence. However, several hindrances continue to slow its adoption and limit accessibility. Uterine fibroids often cause heavy menstrual bleeding, pelvic pain, and fertility challenges, making effective treatment critical. Identifying and addressing these hindrances is vital for healthcare providers, pharmaceutical companies, and device manufacturers seeking to expand their reach and improve patient outcomes.
High Cost of Advanced Treatments
The cost of advanced treatment options, such as MRI-guided focused ultrasound, robotic-assisted surgeries, and uterine artery embolization, remains a significant hindrance. These procedures, while effective and minimally invasive, require substantial financial investment, limiting access for patients, particularly in low- and middle-income regions.
Limited Patient Awareness
Many women are unaware of the full spectrum of treatment options available, including non-invasive procedures, pharmacological therapies, and fertility-preserving interventions. Lack of awareness can lead to delayed diagnosis and treatment, which reduces adoption of modern therapies and slows market growth.
Regulatory and Approval Complexities
The process of obtaining regulatory approval for new devices and drugs can be lengthy and complex, varying across regions. This hinders the introduction of innovative treatments, delays their availability to patients, and acts as a barrier to market expansion.
Inconsistent Insurance and Reimbursement
Limited insurance coverage and reimbursement for advanced treatments represent another major hindrance. Many patients face high out-of-pocket costs for minimally invasive procedures or new pharmacological therapies, restricting adoption and slowing overall market growth.
Shortages in Infrastructure and Skilled Personnel
Advanced treatment options require specialized equipment and trained healthcare professionals, which may be lacking in rural areas and emerging markets. This infrastructure and skill gap restricts access to effective therapies and limits market penetration.
Cultural and Social Barriers
Cultural norms and societal stigma surrounding gynecological conditions can prevent women from seeking timely treatment. Embarrassment, misconceptions, or social pressures may delay medical intervention, reducing adoption of effective therapies and hindering market growth.
Geographic Disparities in Access
Urban-rural disparities impact accessibility to advanced therapies. Metropolitan areas may have well-equipped medical facilities offering modern procedures, whereas rural regions often rely on conventional surgeries due to limited resources. Bridging this gap is crucial to ensure equitable access and support market growth.
Resistance Among Healthcare Providers
Some healthcare providers may be hesitant to adopt new treatment techniques due to familiarity with conventional methods or lack of proper training. This resistance can limit the availability of innovative therapies to patients, slowing market expansion and reducing treatment adoption.
Conclusion
The uterine fibroid treatment market faces multiple hindrances, including high treatment costs, limited awareness, regulatory challenges, insurance gaps, infrastructure shortages, cultural barriers, and provider resistance. Addressing these obstacles is essential to expand patient access, promote adoption of advanced therapies, and support long-term market growth.