Report Overview:
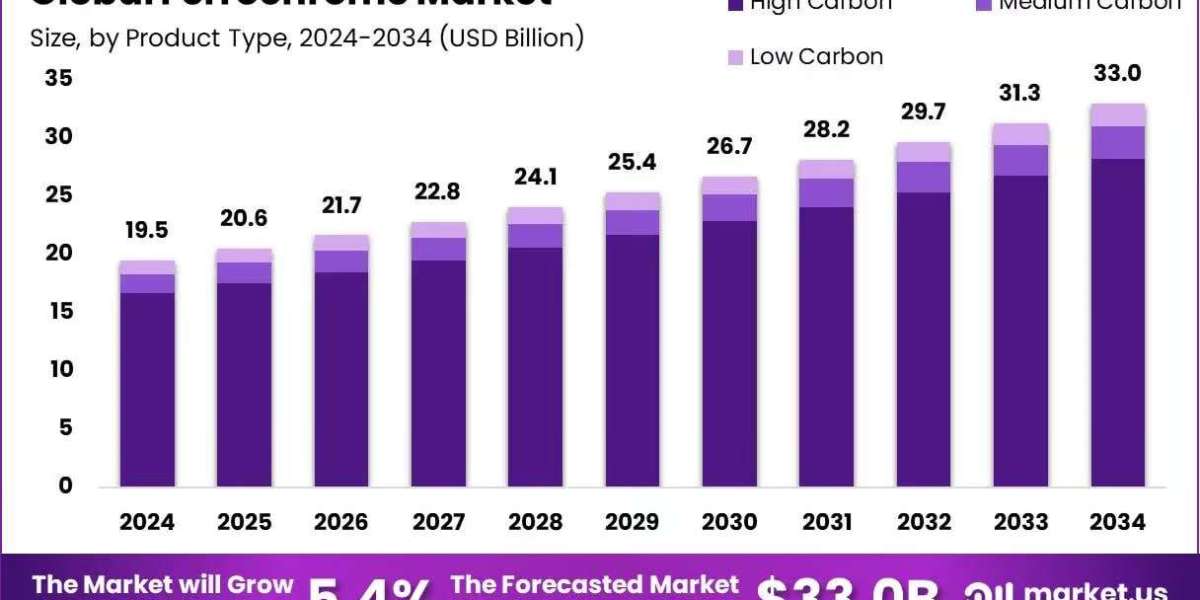
The global ferrochrome market is projected to grow significantly, rising from an estimated USD 19.5 billion in 2024 to approximately USD 33.0 billion by 2034. This growth reflects a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.4% over the forecast period from 2025 to 2034, driven by increasing demand in the stainless steel industry and infrastructure development worldwide.
The global ferrochrome market is experiencing steady growth, fueled by rising demand for stainless steel across sectors like construction, automotive, and industrial manufacturing. Ferrochrome, an essential alloying material in stainless steel production, enhances durability and corrosion resistance making it vital for modern infrastructure. Regions such as Asia-Pacific are leading consumption due to rapid urbanization and industrial expansion. Additionally, environmental pressures are accelerating the shift toward low-carbon ferrochrome and greener production technologies. As sustainability becomes central to steelmaking practices, the ferrochrome market is evolving to align with both economic needs and global climate goals, paving the way for long-term growth.
Key Takeaways:
- The global ferrochrome market was valued at USD 19.5 billion in 2024.
- The global ferrochrome market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 5.4 % and is estimated to reach USD 33.0 billion by 2034.
- Among product types, high carbon accounted for the largest market share of 85.5%.
- Among forms, granules accounted for the majority of the market share at 26.3%.
- By application, stainless steel accounted for the largest market share of 77.8%.
- By end-use, building & construction accounted for the majority of the market share at 46.4%.
- Asia Pacific is estimated as the largest market for ferrochrome with a share of 67.4% of the market share.
Download Exclusive Sample Of This Premium Report:
https://market.us/report/ferrochrome-market/free-sample/
Key Market Segments:
By Product Type
- High Carbon
- Medium Carbon
- Low Carbon
By Form
- Granules
- Powder
- Lumps
By Application
- Stainless steel
- 200 Series
- 300 Series
- 400 Series
- Duplex Series
- Others
- Cast Iron
- Specialty Steel
- Others
By End-Use
- Building & Construction
- Automotive & Transportation
- Consumer Goods
- Mechanical Engineering & Heavy Industries
- Aerospace and Defense
- Others
Drivers
The global ferrochrome market is primarily driven by the rising demand for stainless steel, which relies heavily on ferrochrome as a key alloying material. As economies worldwide expand, especially in Asia-Pacific, Latin America, and Africa, infrastructure projects such as highways, bridges, commercial buildings, and urban housing developments are accelerating. Stainless steel’s strength, corrosion resistance, and durability make it a top choice for these large-scale construction efforts directly increasing the consumption of ferrochrome.
Rapid industrialization is another core factor contributing to this demand. Countries like India and China are scaling up manufacturing and transportation projects, which require large quantities of stainless steel for machinery, railways, and automotive components. This continuous industrial expansion ensures a stable, long-term demand pipeline for ferrochrome producers.
Additionally, the automotive sector is increasingly adopting stainless steel in vehicle components for its ability to withstand heat and corrosion, especially in electric and hybrid vehicles. This creates further growth opportunities for ferrochrome as a core input material.
On the sustainability front, regulatory pressure and growing consumer preference for eco-friendly solutions are prompting manufacturers to explore cleaner ferrochrome production methods. The development of low-carbon ferrochrome (LCFC), which aligns with global carbon-reduction goals, is gaining traction. Governments and industries are both supporting the shift toward “green steel,” boosting investment in LCFC technologies and strengthening the market’s innovation potential.
Restraining Factors
The ferrochrome market, despite its critical role in stainless steel manufacturing, faces considerable restraints that could hamper growth in the long run. Chief among these is the energy- and carbon-intensive nature of ferrochrome production. The process requires high-temperature smelting, typically achieved using electricity or coal, both of which contribute significantly to greenhouse gas emissions. This characteristic places ferrochrome producers under increasing regulatory pressure, particularly in regions such as Europe and South Africa, where environmental legislation is tightening and carbon pricing mechanisms are being enforced more aggressively.
Compliance with these emissions standards adds to operational costs, making production less economically viable in certain locations. For instance, companies may need to invest in emission-reducing technologies or carbon credits, both of which affect profit margins. These rising costs can discourage new investments or expansions, slowing down overall market momentum.
Another major restraint is raw material price volatility especially for chromite ore and electricity. Since these inputs constitute a large portion of production costs, any supply chain disruption or geopolitical instability affecting mining regions can directly impact ferrochrome pricing. These fluctuations add financial uncertainty for manufacturers and may cause delays in production or shipment schedules.
Additionally, logistical challenges and inconsistent power supply in developing economies can further hinder manufacturing efficiency and output reliability. This is especially true in regions where electricity infrastructure is underdeveloped or unreliable, leading to downtime or production losses.
Opportunities
One of the most exciting growth avenues in the ferrochrome market is the emergence of low-carbon ferrochrome (LCFC). As countries enforce stricter carbon-emission norms, steelmakers are actively seeking cleaner alternatives to traditional ferroalloys. LCFC fits perfectly into this shift, aligning with global carbon-neutrality goals. Moreover, the development of hydrogen-based and electrified smelting techniques offers a promising route to drastically reduce the carbon footprint associated with ferrochrome production. There is also expanding interest in applying ferrochrome in specialty alloys that are used in critical industries like aerospace and marine engineering. These sectors demand materials that can withstand extreme conditions while maintaining structural integrity making ferrochrome-based alloys highly suitable and opening up new niche opportunities for manufacturers.
The market is brimming with opportunities, especially around the evolution of low-carbon ferrochrome. With global climate change initiatives and carbon reduction strategies gaining traction, there's a strong incentive for industries to pivot toward sustainable practices. LCFC emerges as a timely solution, offering a cleaner path for steelmakers aiming to reduce emissions without compromising on alloy quality. Advancements in hydrogen-fueled and electric smelting technologies are accelerating this shift, enabling manufacturers to create greener ferrochrome with significantly lower environmental impact.
This technological shift aligns well with international decarbonization goals and regulatory support in both developed and emerging markets. Furthermore, the application scope of ferrochrome is widening. Beyond traditional stainless steel, there is growing demand in specialty alloys used in marine and aerospace sectors. These environments require materials with superior thermal stability, corrosion resistance, and tensile strength qualities ferrochrome alloys naturally possess. These niche applications promise new revenue streams and strategic growth areas for the market.
Trends
The ferrochrome market is undergoing a dynamic transformation driven by evolving industrial demands, sustainability goals, and technological innovation. A dominant trend is the continued preference for high-carbon ferrochrome, primarily due to its cost-effectiveness and compatibility with stainless steel production. It remains the most widely used grade, particularly in mass-scale infrastructure and industrial projects, where affordability and durability are key.
Simultaneously, there is a growing shift toward granular ferrochrome. Unlike lump or briquette forms, granular ferrochrome is easier to handle, store, and mix during steelmaking, offering higher operational efficiency. This trend reflects the industry’s push for process optimization and better material control in steel production plants.
Geographically, Asia-Pacific continues to dominate the ferrochrome market, with countries like China, India, and South Korea investing heavily in infrastructure development, manufacturing capacity, and urbanization projects. Their increasing demand for stainless steel fuels steady consumption of ferrochrome in this region, making it the global demand center.
Additionally, circular economy practices are slowly entering the ferrochrome sector. More companies are exploring recycling and reuse of chromium from scrap metals, which can reduce dependency on virgin raw materials and lower environmental impact.
Market Key Players:
- Samancor Chrome
- Eurasian Resources Group
- Hernic
- Vargön Alloys AB
- Ferbasa
- Yilmaden
- Glencore
- ALBCHROME
- Outokumpu
- IMFA
- Balasore Alloys Limited
- Ferro Alloys Corporation
- Indiano Chrome Pvt Ltd
- Other Key Players
Conclusion
The global ferrochrome market stands at a pivotal point of transformation, driven by expanding industrialization, rapid urban growth, and the ever-growing demand for stainless steel in construction, automotive, and infrastructure sectors. Its integral role in enhancing the durability and strength of steel makes ferrochrome a cornerstone material for modern development. Simultaneously, environmental concerns and policy shifts are encouraging the transition toward more sustainable solutions, such as low-carbon ferrochrome and cleaner smelting technologies.
Looking ahead, the market is expected to benefit from both traditional applications and emerging opportunities in specialty alloys and green manufacturing. However, it must also address production-related challenges, including energy consumption, raw material cost fluctuations, and tightening emission regulations. As industries worldwide move toward more sustainable practices, ferrochrome’s future growth will depend on balancing efficiency, innovation, and environmental compliance. With the right investments and technological adaptations, the ferrochrome industry is well-positioned for long-term, responsible growth.