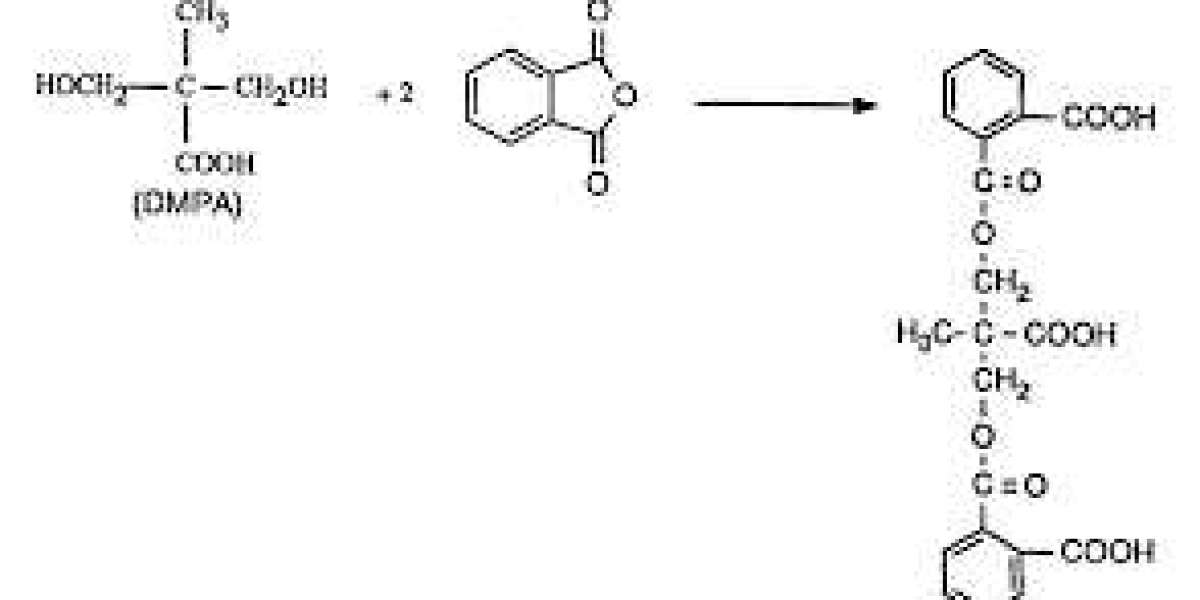
The Dimethylolpropionic Acid (DMPA) market faces an increasingly complex web of challenges that threaten growth trajectories across global regions and end-use sectors. While demand for DMPA remains high, particularly in waterborne polyurethane and resin systems, the industry is constrained by several inhibitors. These include raw material volatility, regulatory hurdles, inconsistent supply chains, and limited production scalability. Navigating these challenges calls for a deliberate strategy built on robust risk mitigation, innovation, and agile business practices. Market players that successfully anticipate and adapt to these barriers can preserve profitability while sustaining long-term market presence.
Raw Material Price Volatility
One of the most pressing growth inhibitors in the DMPA market is the unpredictable pricing of key raw materials such as neopentyl glycol and dimethylolpropionic precursors. These inputs are directly linked to global petrochemical trends and energy markets, which are often destabilized by geopolitical disruptions or oil price swings. This volatility raises production costs, reduces forecasting accuracy, and forces manufacturers to constantly renegotiate supplier terms. To counter this, companies are adopting hedging strategies and maintaining buffer stocks of critical raw materials. Developing alternate sourcing relationships and leveraging global procurement networks also help minimize exposure to cost shocks.
Supply Chain Disruptions and Geographic Risk
Disruptions caused by global events — including port congestion, geopolitical conflict, or trade sanctions — significantly impact the timely availability of DMPA and its ingredients. For instance, COVID-era shipping bottlenecks led to widespread delivery delays, affecting manufacturers relying on just-in-time inventory models. Moreover, overdependence on a few major producing countries exposes buyers to regional risks. To mitigate this, firms are redesigning supply chains to include nearshoring, multi-sourcing, and investment in regional storage hubs. By spreading logistical operations across different geographies, companies enhance operational flexibility and reduce vulnerability to single-point failures.
Regulatory and Environmental Compliance Pressures
Environmental regulations such as REACH in Europe and EPA chemical safety assessments in the U.S. are tightening oversight over chemical manufacturing and handling. For DMPA producers, this means higher compliance costs, increased documentation, and sometimes limited approval for end-use applications. Non-compliance can result in product bans or costly reformulation requirements. Additionally, pressure to decarbonize and reduce emissions affects energy-intensive processes common in DMPA synthesis. To navigate this, manufacturers are investing in greener production technologies, such as water-based synthesis routes, and seeking third-party certifications that demonstrate environmental stewardship. Regulatory forecasting and scenario modeling are also being used to anticipate and adapt to evolving policies.
Technological Obsolescence and Innovation Gaps
Another critical risk involves technological stagnation. In an industry where downstream users demand more efficient, high-performance, and eco-friendly products, a failure to innovate can quickly erode market relevance. Some DMPA producers have been slow to diversify their offerings or improve production scalability through automation and digital process optimization. Companies that underinvest in R&D risk falling behind as competitors introduce modified DMPA grades tailored for niche applications such as biomedical polymers, high-durability coatings, or 3D printing resins. To remain competitive, businesses are establishing partnerships with research institutions and allocating greater resources toward process innovation and product development.
Limited End-Use Diversification
While DMPA’s primary applications lie in waterborne polyurethane dispersions and resin systems, limited diversification in downstream usage can restrict market growth. An overconcentration in construction or automotive coatings, for example, leaves the industry vulnerable to downturns in those specific sectors. Sluggish investment in new application development reduces market agility and suppresses broader adoption. Mitigating this requires aggressive expansion into adjacent markets such as textile coatings, leather finishing, electronics encapsulation, and medical adhesives. Customizing DMPA derivatives to meet the technical demands of these emerging applications can buffer against sector-specific downturns.
Intellectual Property Barriers and Market Entry Complexity
High barriers to entry — particularly regarding proprietary formulations and intellectual property — limit participation in the DMPA market and slow competitive expansion. New entrants face challenges in acquiring licenses, scaling processes, or matching the consistency and quality of incumbents' offerings. These hurdles can stifle innovation and delay the market penetration of alternative producers who might otherwise drive down prices and broaden product availability. To ease this friction, collaboration models such as technology transfer agreements, contract manufacturing partnerships, and open innovation frameworks are being explored to stimulate healthy competition and cross-pollination of ideas.
Talent Shortages and Workforce Disruption
The chemical industry is experiencing a global talent gap, particularly in skilled labor, process engineering, and safety compliance roles. For DMPA producers, this shortage undermines operational efficiency, delays plant expansions, and increases the cost of recruitment and training. Labor-intensive operations are also more prone to disruptions due to absenteeism or turnover. Risk mitigation here involves strategic workforce planning, investment in automation, and the development of digital twin environments for safer and more efficient operations. Upskilling programs and knowledge-sharing platforms further strengthen internal capabilities and reduce reliance on external expertise.
Conclusion: Building Resilience for Sustainable Growth
The DMPA market faces an array of structural and cyclical challenges, but these growth inhibitors are not insurmountable. Forward-thinking companies are adopting a mix of procurement agility, regulatory foresight, technological modernization, and workforce resilience to mitigate risks and unlock new opportunities. By staying attuned to evolving end-user needs and proactively addressing vulnerabilities, market participants can sustain competitive positioning and chart a path toward long-term, risk-adjusted growth in the DMPA industry.