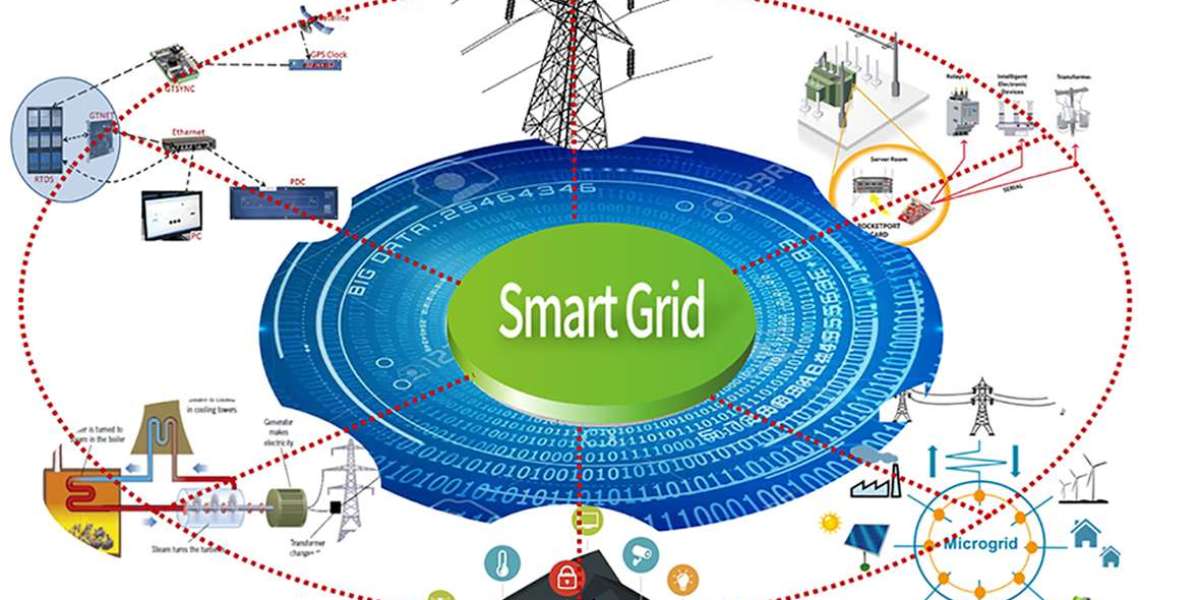
The smart grid sensor market has emerged as a pivotal component in the evolution of modern electrical grids. With the growing demand for energy efficiency, reliability, and integration of renewable energy sources, smart grid sensors are at the forefront of enabling intelligent energy management systems worldwide. These sensors play a critical role in monitoring, controlling, and optimizing the performance of electrical grids, making them smarter and more adaptive.
Market Drivers
One of the primary drivers propelling the smart grid sensor market is the global push towards renewable energy integration. Traditional power grids face challenges in handling the intermittent nature of renewable energy such as solar and wind. Smart grid sensors provide real-time data on energy generation, consumption, and grid stability, allowing grid operators to balance supply and demand efficiently.
Additionally, the rising adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) increases the complexity of electricity demand patterns. Smart grid sensors help manage this complexity by providing accurate load forecasting and enabling dynamic load management, thus preventing grid overloads and enhancing grid reliability.
Government initiatives and regulatory frameworks aimed at reducing carbon emissions also significantly contribute to the growth of the smart grid sensor market. Many countries are investing heavily in modernizing their grid infrastructure, incorporating smart sensors as a foundational technology to ensure energy efficiency and sustainability.
Technological Advancements
Advances in sensor technology, including miniaturization, wireless communication, and enhanced data processing capabilities, are transforming the market. Modern smart grid sensors are equipped with IoT (Internet of Things) connectivity, enabling seamless data transmission to centralized control centers. This real-time data allows for predictive maintenance, fault detection, and quicker restoration during outages.
Moreover, the integration of AI and machine learning with sensor data analytics is enhancing grid management. These technologies allow for the identification of usage patterns, early detection of faults, and optimization of grid operations, which significantly reduce downtime and operational costs.
Market Segmentation
The smart grid sensor market can be segmented based on type, application, and region. Sensor types include voltage sensors, current sensors, temperature sensors, and others. Each sensor type offers unique capabilities for different grid functions such as monitoring power quality, detecting faults, and managing loads.
Applications of smart grid sensors span distribution automation, transmission monitoring, substation automation, and demand response management. Distribution automation, in particular, is a rapidly growing segment, as utilities seek to enhance the efficiency of electricity delivery and reduce losses.
Geographically, North America and Europe lead the smart grid sensor market, driven by high infrastructure investments and early adoption of smart grid technologies. However, the Asia-Pacific region is witnessing the fastest growth due to rapid urbanization, increasing electricity demand, and significant government spending on smart grid projects.
Challenges
Despite the promising growth, the smart grid sensor market faces challenges. High initial deployment costs can deter smaller utilities from adopting smart grid technologies. Additionally, the integration of sensors with legacy grid systems poses technical challenges and requires substantial investment in upgrading existing infrastructure.
Data security and privacy concerns also remain significant barriers. As smart grid sensors rely heavily on wireless communication and cloud-based data processing, the risk of cyber-attacks increases. Ensuring robust cybersecurity measures is crucial for maintaining the integrity and reliability of smart grids.
Future Outlook
Looking ahead, the smart grid sensor market is poised for robust expansion. The growing trend toward decentralization of power generation, including the rise of microgrids and prosumer participation (consumers who also generate energy), necessitates more advanced and widespread sensor deployments.
Emerging technologies such as 5G connectivity will further enhance the capabilities of smart grid sensors by providing faster and more reliable communication channels. This will enable better real-time monitoring and more responsive grid management.
Collaborations between technology providers, utilities, and governments are expected to increase, fostering innovation and accelerating the deployment of smart grid sensors globally. The convergence of IoT, AI, and advanced sensor technologies will transform traditional power grids into highly resilient, efficient, and sustainable smart grids.
Conclusion
The smart grid sensor market is integral to the modernization of power grids, offering solutions that address the challenges of energy management in the 21st century. With increasing emphasis on sustainability, energy efficiency, and grid reliability, smart grid sensors will continue to drive innovation and growth in the energy sector, paving the way for a smarter, cleaner, and more reliable power future.