In the modern healthcare landscape, technological advancements are rapidly reshaping the way medical professionals approach patient care. One area experiencing significant transformation is surgery. Surgical Information Systems Market (SIS) are increasingly becoming integral tools in surgical environments, providing a wealth of opportunities to improve efficiency, safety, and patient outcomes. As healthcare institutions continue to embrace digital technologies, the expansion of SIS is poised to revolutionize surgical practices on a global scale.
Surgical Information Systems encompass a broad range of digital tools designed to streamline the management, storage, and sharing of surgical data. These systems collect, organize, and display crucial information throughout the surgical process, ensuring that healthcare providers have real-time access to the data they need to make informed decisions. While SIS adoption is still growing, the expansion of these systems promises to bring about a new era of surgery characterized by better patient outcomes, improved efficiency, and greater collaboration among medical professionals.
Bridging the Gap in Surgical Efficiency
The expansion of Surgical Information Systems offers significant potential to bridge the gaps in surgical efficiency. Traditional surgical settings often rely on paper-based records, verbal communication, and fragmented workflows. This can lead to delays, miscommunications, and increased potential for errors, all of which impact the quality of care delivered to patients.
By adopting SIS, hospitals and surgical centers can streamline their workflows, enabling healthcare teams to collaborate seamlessly in real-time. With centralized access to all relevant patient data—from preoperative assessments to surgical history and imaging results—surgeons, anesthesiologists, and other team members are better equipped to make timely, well-informed decisions. This increased accessibility leads to fewer delays in procedures and a more organized approach to surgery. Additionally, with the ability to access data instantly, surgical teams can react more quickly to complications, reducing the likelihood of errors and improving patient safety.
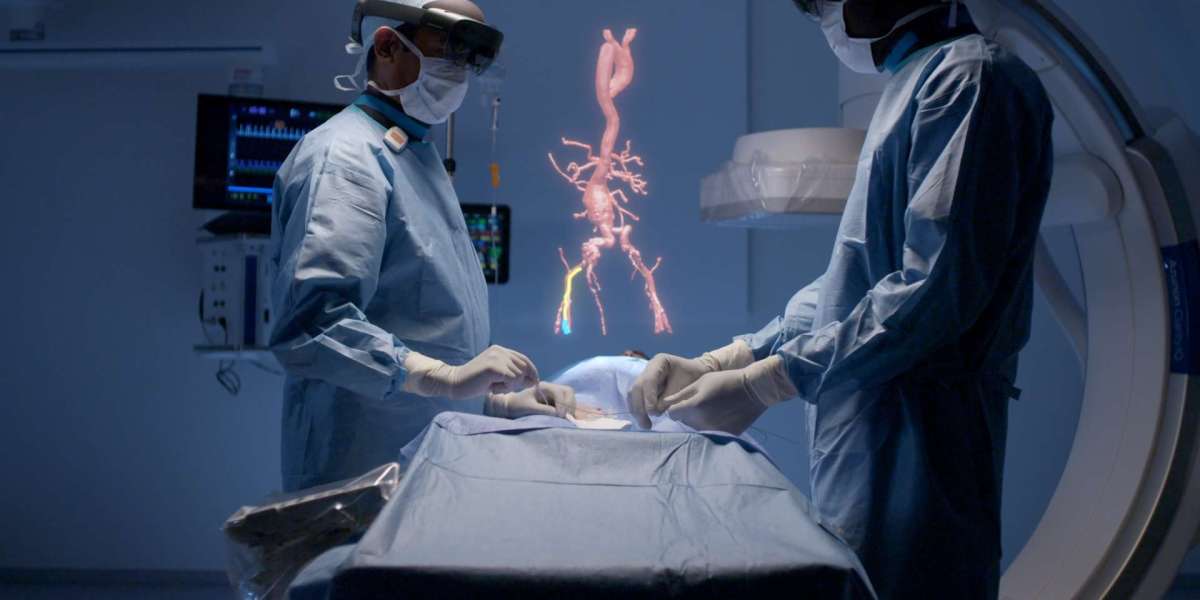
Enhancing Surgical Precision and Decision-Making
The growing adoption and expansion of SIS offer considerable advancements in surgical precision. Precision is critical in surgery, and even the slightest misstep can lead to complications for the patient. SIS systems provide an integrated platform for various technologies, including imaging systems (such as CT scans, MRIs, and X-rays), surgical planning tools, and patient monitoring systems.
As these systems continue to expand, they enable surgeons to plan and execute surgeries with greater accuracy. For instance, surgeons can use real-time imaging data to guide their actions during the procedure, ensuring they operate on the correct area and avoid sensitive structures. Furthermore, predictive analytics integrated into SIS platforms can help surgeons anticipate complications before they arise. This ability to plan more precisely and foresee challenges enhances the overall effectiveness of surgeries, leading to better patient outcomes and faster recovery times.
Moreover, the data provided by SIS allows surgeons to collaborate more effectively. Remote consultations and tele-surgery capabilities are becoming increasingly common, enabling specialists to participate in surgeries without being physically present. As the technology expands, the ability to connect surgeons from different parts of the world creates a new level of expertise-sharing and collaboration that would have been unimaginable just a few decades ago.
Improving Patient Safety Through Real-Time Monitoring
Patient safety is a primary concern in surgery, and the expansion of SIS is contributing significantly to minimizing risks during procedures. SIS platforms can monitor a wide range of parameters during surgery, such as the patient’s vital signs, anesthesia levels, and surgical instruments in use. This real-time monitoring allows healthcare professionals to quickly detect any abnormalities and respond immediately to prevent serious complications.
For example, if a patient's blood pressure drops unexpectedly or a surgical tool is not accounted for during the procedure, the system will alert the surgical team. With these alerts in place, the team can act swiftly to address any issues, preventing them from escalating into life-threatening situations. Furthermore, by tracking surgical instruments and ensuring that no items are left inside the patient after surgery, SIS helps reduce the risk of postoperative complications, such as infections or the need for additional surgeries.
The expansion of real-time monitoring and alerting systems within SIS also offers a valuable opportunity for continuous quality improvement. By collecting data on surgical outcomes, complications, and patient recovery, hospitals can gain insights into the performance of their surgical teams. This information can be used to identify trends, improve training, and optimize surgical procedures, all of which contribute to better patient safety and care.
Expanding Access to High-Quality Surgery
Surgical Information Systems are also playing a critical role in expanding access to high-quality surgical care, particularly in underserved regions. Telemedicine and remote surgical monitoring, integrated into SIS, are enabling healthcare providers to extend their expertise to areas that may lack specialized surgical resources. Through remote consultations and virtual surgical planning, surgeons can collaborate with local healthcare providers to offer guidance and support, ensuring that patients in remote areas receive the best possible care.
The expansion of SIS has the potential to democratize surgical care by providing more equitable access to specialists. Surgeons in rural or low-resource settings can now access the knowledge and support of highly skilled professionals from around the world, significantly improving outcomes for patients who might otherwise not have access to such expertise.
Facilitating Data-Driven Decision-Making
As SIS expands, the wealth of data it generates provides invaluable insights for continuous improvement in surgical practices. Data analytics capabilities are at the core of SIS, allowing hospitals to collect and analyze vast amounts of surgical data, such as patient demographics, surgical outcomes, complication rates, and recovery times. This data-driven approach enables hospitals to identify patterns, optimize surgical procedures, and establish best practices.
Hospitals can also use this data to track the performance of individual surgeons and surgical teams. By assessing their strengths and areas for improvement, healthcare providers can offer targeted training and feedback to enhance surgical techniques and overall performance. This focus on continuous improvement contributes to better patient outcomes and increases the overall efficiency of surgical departments.
Conclusion: The Future of Surgery is Digital
The expansion of Surgical Information Systems is transforming the landscape of surgery, offering new opportunities for improved efficiency, precision, patient safety, and access to care. As technology continues to evolve, SIS platforms will become more sophisticated, integrated, and accessible. The growing use of data analytics, real-time monitoring, and telemedicine capabilities promises to usher in a new era of smarter, safer, and more collaborative surgeries.
For healthcare providers, embracing the expansion of SIS is not just a matter of adopting new technology—it is an investment in the future of surgery. By integrating these systems into surgical workflows, hospitals can enhance their ability to deliver high-quality care to patients while also improving operational efficiency. As the adoption of SIS continues to grow, the potential for positive change in the surgical field is limitless, ultimately leading to better outcomes for patients worldwide.