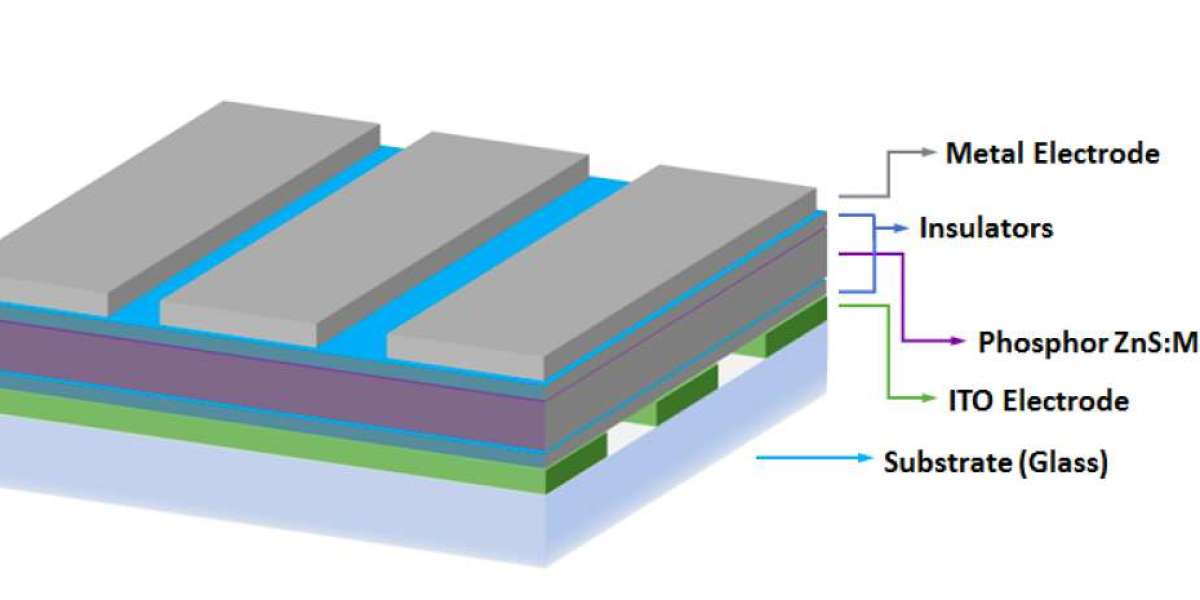
The thin-film encapsulation (TFE) market is witnessing rapid growth, driven by an increasing demand for flexible electronics, OLED displays, and solar panels. However, the market faces several challenges that could potentially hinder its progress. These challenges include high production costs, material limitations, and technical complexities in scaling up manufacturing processes. While the market is expanding, it must overcome these obstacles to sustain long-term growth and achieve widespread adoption across different industries.
1. High Production Costs
The production of thin-film encapsulation materials involves the use of specialized equipment and advanced technologies, such as atomic layer deposition (ALD) and physical vapor deposition (PVD). These technologies, while efficient, are costly due to their high precision and sophisticated machinery. The materials themselves, including inorganic and organic barrier films, can also be expensive. These high costs, which are passed on to manufacturers, can limit the adoption of TFE in mass-market products, especially in cost-sensitive industries like consumer electronics. Additionally, small-scale manufacturers may struggle to afford the upfront investment required for TFE production, leading to slower market penetration.
2. Scalability of Manufacturing Processes
Scaling up TFE production to meet the demands of large-scale commercial applications remains a significant challenge. While laboratory-scale production of thin-film encapsulation is well-established, transitioning to large-scale production while maintaining the same level of quality and performance is difficult. Technologies like ALD, which offer precise layer deposition, are slower and require expensive machinery for high-volume production. As a result, it can be difficult for manufacturers to produce TFE materials at a speed that meets the needs of industries like electronics, solar energy, and automotive without incurring high operational costs.
3. Limited Material Availability and Performance Issues
While there has been progress in the development of thin-film encapsulation materials, there are still limitations regarding the availability of suitable materials that provide optimal performance. Materials used for TFE, such as silicon nitride and aluminum oxide, are often difficult to produce in large quantities, which can result in supply shortages. Furthermore, not all materials meet the required performance criteria, such as high moisture and oxygen barrier properties, long-term stability, and flexibility. Developing new materials that can address these issues while remaining cost-effective is a challenge that needs to be solved to fully capitalize on the potential of the thin-film encapsulation market.
4. Complexity in Maintaining Long-Term Stability
One of the main reasons for the adoption of thin-film encapsulation is to enhance the durability and performance of sensitive electronics, particularly in OLED displays and solar cells. However, ensuring long-term stability of thin-film materials in various environmental conditions remains a challenge. Thin-film encapsulation must protect devices from moisture, oxygen, and mechanical stress over an extended period without degrading the performance of the encapsulated electronics. Over time, factors such as temperature fluctuations, UV exposure, and mechanical strain can compromise the protective properties of the thin films, leading to failure and potential device malfunction. Researchers are working to enhance the long-term stability of TFE materials, but it is an ongoing challenge.
5. Environmental Concerns and Sustainability
As the demand for thin-film encapsulation grows, the environmental impact of its production and disposal becomes a concern. The materials used in thin-film encapsulation, particularly those with inorganic components, may be difficult to recycle or dispose of sustainably. This creates a need for research into environmentally friendly alternatives that can provide the same level of protection while being more eco-friendly. The push for sustainability in manufacturing processes, coupled with the increasing regulatory focus on reducing waste and pollution, poses a significant challenge to manufacturers in the TFE market. Moving toward green technologies and materials is essential for the long-term success of the thin-film encapsulation market.
6. Competition from Alternative Encapsulation Technologies
While thin-film encapsulation is a leading solution for protecting sensitive electronics, it faces competition from alternative encapsulation technologies. One such competitor is traditional glass-based encapsulation, which has been widely used for protecting OLED displays and solar cells. Glass encapsulation offers higher durability and long-term stability but lacks flexibility and can be heavy and brittle. However, some industries may still prefer glass over thin films due to its established reliability. The ability of thin-film encapsulation to compete effectively with alternative materials, such as glass and plastics, is vital to the future success of the TFE market.
7. Technological Advancements and Adoption Barriers
The market for thin-film encapsulation relies heavily on advanced technologies like ALD, PVD, and chemical vapor deposition (CVD) to achieve the high precision required for encapsulation. While these technologies continue to improve, their complexity can pose a barrier to entry for new manufacturers and smaller companies that lack the technical expertise and financial resources. Additionally, the adoption of newer technologies by industries that rely on encapsulation solutions is often slow, as companies may be hesitant to switch from well-established practices to cutting-edge technologies. Overcoming this inertia is critical for the TFE market to expand further.
8. Regulatory and Standardization Challenges
As with any emerging technology, regulatory hurdles and the lack of standardized practices can hinder the growth of the thin-film encapsulation (TFE) market. Regulatory bodies across different regions may have varying requirements for the use of thin-film materials in consumer electronics, solar panels, and other applications. The lack of consistent global standards for thin-film encapsulation could slow down adoption, as manufacturers may have to adapt their processes to meet regional regulations. Developing universal standards for TFE materials and processes would help streamline production and foster market growth.