The processed meat market is an essential part of the global food industry, but it is not without its pain points. These challenges stem from a variety of factors, including consumer preferences, regulatory hurdles, environmental concerns, rising costs, and competition from alternative products. As the market continues to evolve, these pain points present significant obstacles for companies trying to stay competitive while maintaining profitability. In this article, we will explore some of the key pain points facing the processed meat market and the strategies that companies may adopt to address them.
Health and Nutrition Concerns
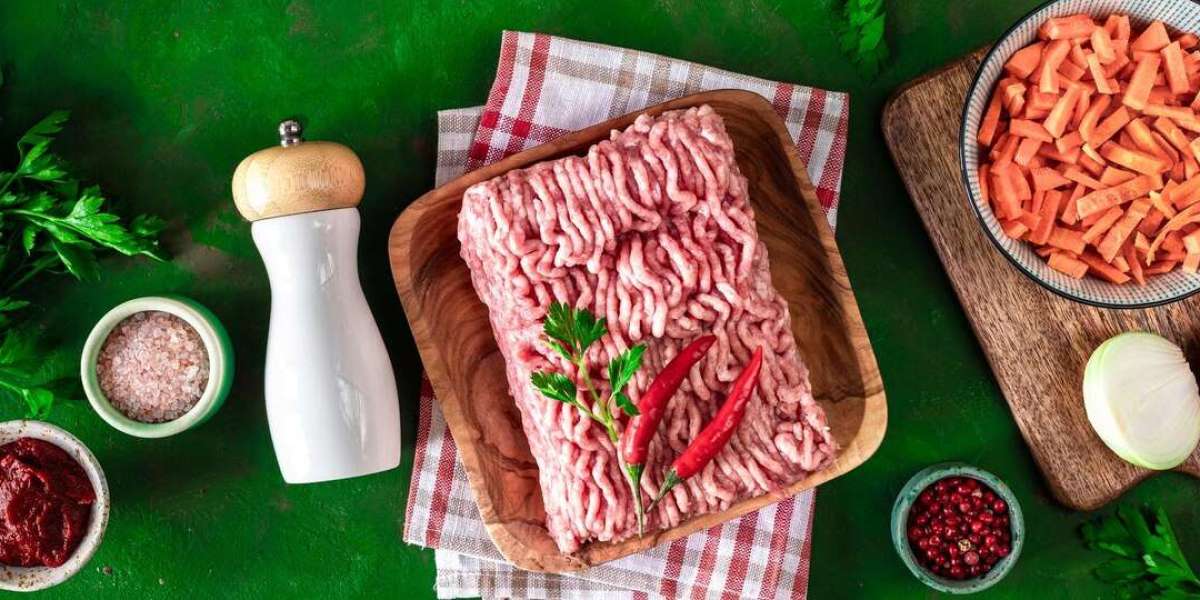
One of the most prominent pain points in the processed meat market is the growing consumer concern over health and nutrition. Processed meats, including sausages, bacon, hot dogs, and deli meats, have been linked to an increased risk of heart disease, cancer, and other chronic illnesses due to their high levels of sodium, nitrates, and unhealthy fats. As consumers become more health-conscious, they are seeking alternatives to traditional processed meats that are lower in fat, sodium, and preservatives.
This growing awareness about the negative health effects of processed meats has resulted in declining consumption in some markets, particularly among younger and more health-conscious consumers. The demand for healthier food options is forcing meat producers to adapt by developing leaner, more natural alternatives. However, overcoming the negative health perception of processed meats remains a challenge for companies in this sector.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability Issues
Another significant pain point for the processed meat market is its environmental impact. The meat industry is a major contributor to greenhouse gas emissions, deforestation, and water usage. As climate change becomes an increasingly urgent global issue, consumers and governments are pushing for more sustainable practices in food production. The processed meat market, which is inherently resource-intensive, is under pressure to reduce its carbon footprint and adopt more sustainable practices.
Manufacturers are being called upon to reduce waste, source meat from farms that follow ethical and eco-friendly practices, and use renewable energy sources in production. However, implementing these changes can be costly and logistically challenging. The environmental impact of meat production also presents a competitive disadvantage for processed meat in comparison to plant-based alternatives, which are typically seen as more sustainable. Companies in the processed meat market must find ways to balance environmental responsibility with profitability in order to remain viable in an increasingly eco-conscious market.
Regulatory Challenges and Compliance
The processed meat market also faces regulatory challenges that can create significant pain points for businesses. Governments around the world are implementing stricter regulations regarding the labeling, marketing, and production of processed meat products. In many regions, there are regulations requiring companies to disclose more information about the nutritional content of their products, including the levels of sodium, fats, and preservatives.
In addition to stricter labeling regulations, there is also an increasing number of government initiatives that aim to reduce the consumption of processed meats. For example, some countries have introduced taxes on processed meats or are considering similar measures to discourage consumption due to health concerns. These regulations increase the cost of compliance for companies, which may require them to reformulate their products or adopt new production processes to meet health and safety standards.
Rising Raw Material and Production Costs
Rising raw material costs are another pain point that processed meat companies are grappling with. Fluctuations in the price of livestock, feed, and other essential ingredients can significantly impact production costs. Events such as disease outbreaks among livestock, extreme weather conditions, or geopolitical instability can cause raw material prices to skyrocket, making it difficult for companies to maintain profitability while keeping product prices competitive.
Additionally, the cost of labor and operational expenses in production facilities is on the rise. As wages and energy costs increase, companies are under pressure to find cost-effective solutions to maintain their bottom lines. To mitigate the impact of rising raw material costs, many processed meat companies are exploring alternative protein sources or investing in automation technologies to reduce labor costs and increase efficiency.
Competition from Plant-Based and Alternative Proteins
The rise of plant-based and alternative proteins has emerged as a major pain point for the processed meat market. Consumers are increasingly seeking plant-based options due to health concerns, ethical considerations regarding animal welfare, and environmental sustainability. Brands such as Beyond Meat, Impossible Foods, and other plant-based protein producers are gaining market share by offering products that closely resemble the taste, texture, and appearance of traditional meat.
For processed meat producers, this shift toward plant-based alternatives presents a significant challenge. Not only are plant-based products often seen as healthier and more sustainable, but they are also increasingly priced competitively with traditional processed meats. This shift in consumer behavior is forcing traditional meat producers to innovate by either developing plant-based products themselves or focusing on creating more sustainable, ethically sourced, and health-conscious processed meat options.
Supply Chain Disruptions
The processed meat market is highly dependent on complex supply chains that stretch across multiple regions. Disruptions to these supply chains can create significant pain points for manufacturers. Natural disasters, transportation delays, labor shortages, and geopolitical tensions can all result in supply chain inefficiencies, leading to product shortages and increased costs.
The COVID-19 pandemic exposed vulnerabilities in the global supply chain, with many meat-processing plants shutting down or operating at reduced capacity. The ripple effects of these disruptions continue to impact the industry today, highlighting the need for processed meat companies to adopt more resilient and flexible supply chain strategies to mitigate risks.
Conclusion
The processed meat market is facing several pain points that require companies to adapt and innovate in order to remain competitive. Health concerns, environmental issues, regulatory challenges, rising raw material costs, and competition from plant-based alternatives are all factors that are shaping the industry’s future. While these barriers present significant challenges, they also create opportunities for companies to differentiate themselves by offering healthier, more sustainable, and cost-effective products. The companies that are able to navigate these pain points successfully will be best positioned to thrive in an ever-evolving market.