Renal Anemia Market Outlook
Around 1 in 7 individuals with kidney disease also experience anaemia, impacting millions of adults worldwide. In the United States alone, over 37 million adults may be affected by chronic kidney disease. Renal Anemia Drug Pipeline Analysis The increasing prevalence of renal anaemia is linked to factors such as unhealthy diets, sedentary lifestyles, and excessive alcohol intake. These challenges have driven pharmaceutical companies to prioritise the development of advanced therapies, leading to a growing pipeline of innovative treatments for improved disease management.
Get a Free Sample Report with a Table of Contents: https://www.expertmarketresearch.com/clinical-trials/renal-anemia-drug-pipeline-insight/requestsample
Renal Anemia: Introduction
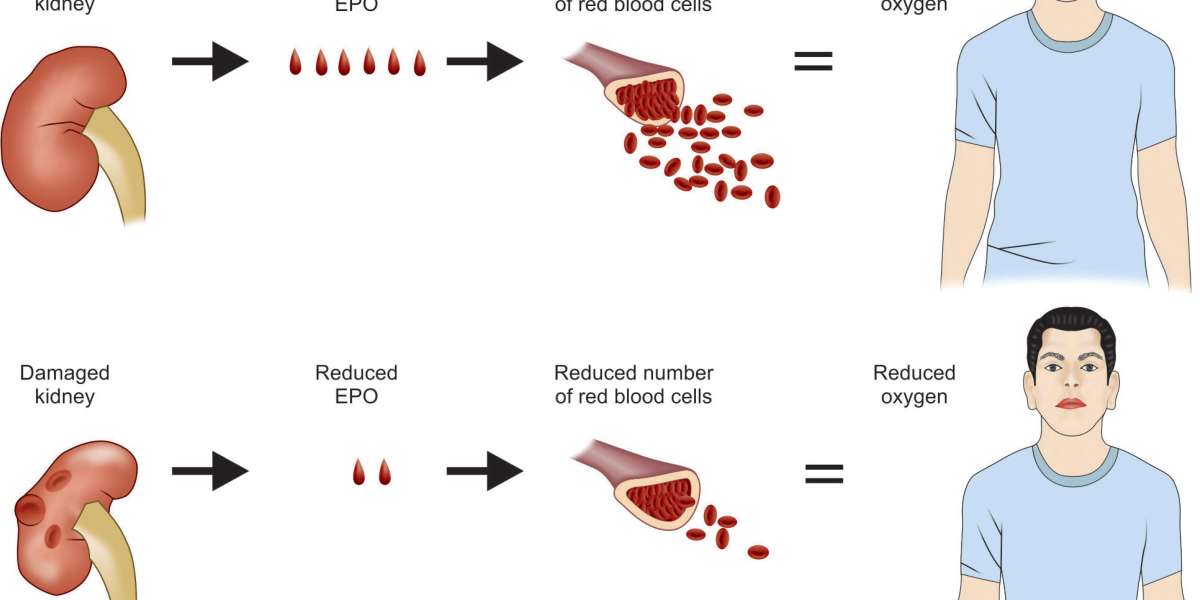
Renal anaemia is a condition commonly associated with chronic kidney disease (CKD), caused by insufficient production of erythropoietin, a hormone essential for red blood cell production. This results in reduced oxygen delivery to tissues, leading to fatigue, weakness, and a higher risk of cardiovascular complications. If left untreated, renal anaemia can severely impact the quality of life. Current therapies include erythropoiesis-stimulating agents and iron supplementation to manage symptoms. Ongoing research focuses on innovative treatments, such as hypoxia-inducible factor stabilisers, to improve efficacy and address unmet needs in managing this condition.
Renal Anemia Treatment Overview
Renal anaemia is a condition associated with chronic kidney disease (CKD), where decreased erythropoietin production leads to low red blood cell counts. This results in symptoms such as fatigue, weakness, shortness of breath, and an increased risk of cardiovascular complications. Effective management is essential to improve patient outcomes and quality of life.
Treatment options include erythropoiesis-stimulating agents (ESAs) to stimulate red blood cell production and iron supplements to address deficiencies. Emerging therapies, such as hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF) prolyl hydroxylase inhibitors, aim to offer alternative and innovative solutions for managing renal anaemia with enhanced safety and efficacy.
Read Full Report with Table of Contents: https://www.expertmarketresearch.com/clinical-trials/renal-anemia-drug-pipeline-insight
Drug Pipeline Therapeutic Assessment
Analysis by Route of Administration
1. Oral
2. Parenteral
3. Others
Analysis by Phase
- Preclinical Phase
- Phase I
- Phase II
- Phase III
- Phase IV
Analysis by Drug Class
- Erythropoiesis-Stimulating Agents (ESAs)
- Hypoxia-Inducible Factor Prolyl Hydroxylase Inhibitors (HIF-PHIs)
- Iron Supplements
- Vitamin Supplements
Renal Anemia Drug Classes
Renal anaemia treatments utilise a range of drug classes, each designed to target specific pathways and mechanisms involved in cancer growth and survival. These diverse classes enhance the effectiveness of therapy and contribute to personalised treatment strategies. Understanding these drug classes is essential for optimising patient outcomes.
1. Erythropoiesis-stimulating agents (ESAs)
Erythropoiesis-stimulating agents (ESAs) are synthetic drugs that mimic erythropoietin, a hormone naturally produced by healthy kidneys to regulate red blood cell production. Widely used in the treatment of renal anaemia, ESAs help increase haemoglobin levels, alleviate fatigue, and improve oxygen delivery throughout the body. They are particularly beneficial for patients with chronic kidney disease, helping to enhance quality of life and reduce anaemia-related complications.
2. Hypoxia-inducible factor Prolyl Hydroxylase Inhibitors (HIF-PHIs)
HIF prolyl hydroxylase inhibitors (HIF-PHIs) are a class of oral drugs that stabilise hypoxia-inducible factors, triggering the body’s natural response to low oxygen levels. By promoting the production of endogenous erythropoietin, these therapies stimulate red blood cell production. HIF-PHIs represent a significant advancement in renal anaemia management, offering an effective and less invasive alternative to injectable ESAs while potentially reducing side effects like hypertension.
3. Iron Supplements
Iron supplements play a pivotal role in treating renal anaemia by addressing iron deficiencies that hinder red blood cell production. Available in oral and intravenous forms, these supplements ensure sufficient iron availability for erythropoiesis, enhancing the effectiveness of other therapies like ESAs. Iron supplementation is integral to improving haemoglobin levels and reducing the need for blood transfusions in patients with chronic kidney disease.
4. Vitamin Supplements
Vitamin supplements, particularly vitamin B12 and folic acid, are essential in supporting red blood cell formation in patients with renal anaemia. These supplements correct nutritional deficiencies commonly associated with chronic kidney disease and are often combined with primary therapies to optimise outcomes. Their role in facilitating erythropoiesis helps improve the effectiveness of treatments while addressing coexisting conditions related to anaemia.
Renal Anemia- Pipeline Drug Profiles
This section provides an overview of the various drugs used to treat renal anemia. It covers their classifications, mechanisms of action, and methods of administration, offering essential insights for effective treatment strategies.
1. AND017
AND017 is an innovative HIF prolyl hydroxylase inhibitor that stimulates erythropoiesis by stabilising hypoxia-inducible factors. Designed as an oral therapy, it mimics the body’s response to hypoxia, promoting natural erythropoietin production and improving red blood cell levels. Clinical trials indicate its potential as a safe and effective alternative to ESAs, offering convenience and improved patient adherence in managing renal anaemia.
2. FG-2216
FG-2216 is a novel HIF prolyl hydroxylase inhibitor developed to treat renal anaemia by enhancing endogenous erythropoietin synthesis. Administered orally, it eliminates the need for frequent injections associated with ESAs. Clinical studies have shown promising results in improving haemoglobin levels, making FG-2216 a next-generation therapy for addressing anaemia in patients with chronic kidney disease.
3. Roxadustat
Roxadustat is a first-in-class oral HIF prolyl hydroxylase inhibitor that stimulates the natural production of erythropoietin. It provides an effective alternative to traditional ESAs for managing renal anaemia. By addressing anaemia-related complications such as hypertension and iron deficiency, roxadustat improves haemoglobin levels and overall quality of life. Clinical data support its safety and efficacy, positioning it as a transformative therapy for CKD patients.
4. PEG-EPO Injection
PEG-EPO is a polyethylene glycol-conjugated erythropoietin injection that offers a prolonged duration of action, reducing the frequency of administration. This therapy stimulates red blood cell production effectively and is particularly beneficial for patients requiring long-term anaemia management. Clinical evidence highlights its ability to improve treatment adherence and outcomes, making PEG-EPO a valuable option for managing anaemia in chronic kidney disease.
Renal Anemia: Competitor Landscape
The key features of the report include patent analysis, clinical trials, grants analysis, funding and investment analysis, partnerships, and collaborations analysis by the leading key players. The major companies in the market are as follows:
Hoffmann-La Roche
Hoffmann-La Roche, based in Basel, Switzerland, is a leader in developing innovative therapies for renal anaemia. Its portfolio includes advanced solutions like PEG-EPO and HIF-PHIs, which aim to enhance treatment efficacy and patient convenience. Roche’s research focuses on addressing unmet needs in CKD-related anaemia, improving haemoglobin levels, and reducing the risks associated with conventional therapies.
Astellas Pharma Inc
Astellas Pharma, headquartered in Tokyo, Japan, is committed to advancing treatments for kidney-related disorders, including renal anaemia. Its key product, roxadustat, offers an oral alternative to injectable ESAs, aiming to improve accessibility and convenience. Astellas’ dedication to patient-centred care drives its efforts to provide effective and innovative therapies for CKD patients facing anaemia.
GlaxoSmithKline
GlaxoSmithKline (GSK), headquartered in Brentford, UK, is at the forefront of renal anaemia research, focusing on hypoxia-inducible factor prolyl hydroxylase inhibitors like daprodustat. GSK’s commitment to improving treatment outcomes includes addressing safety and efficacy challenges associated with traditional therapies. Their innovative approach underscores a strong focus on enhancing the quality of life for CKD patients with anaemia.
Other key players in the landscape include Kind Pharmaceuticals LLC, Angde Biotech Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., FibroGen, Bayer, Daiichi Sankyo, and Jiangsu HengRui Medicine Co., Ltd.
We at Expert Market Research always strive to provide you with the latest information. The numbers in the article are only indicative and may be different from the actual report.