With years of experience in the pharmaceutical and life science sectors, CD Bioparticles announces its advanced line of multiplex fluorescence particles designed to streamline complex biological assays in flow cytometry experiments. These particles exhibit low signal widths in the forward scatter, side scatter and fluorescence channels. Various surface modifications, channels and sizes are also supported.
Flow cytometry is a convenient detection technique characterized by high throughput, wide linear range, high accuracy and good reproducibility. Therefore, flow cytometry is widely used in clinical diagnosis and medical research, such as tumor-associated diseases, autoimmune diseases, cardiovascular diseases, inflammatory infections and infectious diseases, providing higher clinical value for differential diagnosis, treatment monitoring and condition assessment.
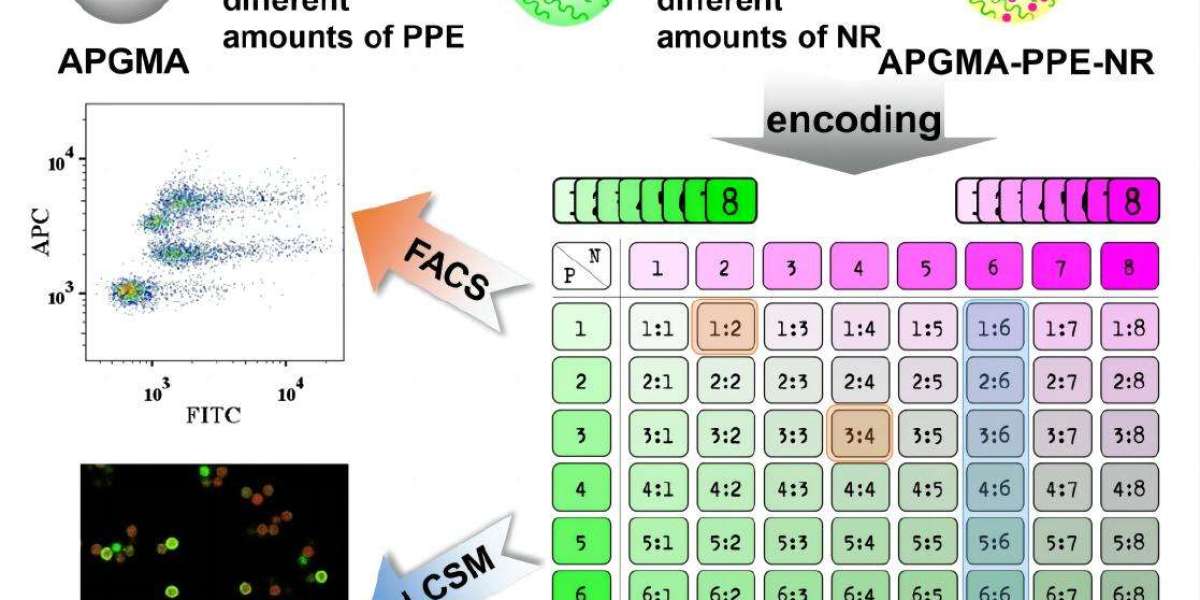
Multiplexed assays allow non-invasive, simultaneous detection of multiple analytes in a single sample. This reduces time and resource consumption compared to traditional methods that necessitate separate tests for each analyte. CD Bioparticles now offers multiple particles with different fluorescence intensities and particle sizes for encoding. These particles with different surface functionalizations can be used in standard flow cytometry or fluorescence-based imaging platforms.
In addition, these particles range in size from 3.0 µm to 15.0 µm and are highly compatible with a wide range of detection methods using universal channels such as FITC, PE, PERCP, DAPI, and APC in small sample sizes. Additionally, multiplex particles enable high throughput analysis with a wide linear range, ensuring highly accurate and reproducible results. By leveraging these innovative particles, scientists can gain valuable insights into complex biological processes with greater efficiency and accuracy.
CD Bioparticles offers a variety of multiplex particles, including Magnetic Multiplex Particles (4.0 µm to 7.5 µm), Dual-color Encoded Multiplex Particles (6.2 µm to 15.0 µm), Functional Multiplex Particles (3.0 µm-15.0 µm), Plain Multiplex Particles, and Protein-Coupled Multiplex Particles. They can be applied in used in a variety of biomedical and optical research, such as multiplex assays, flow cytometry, and fluorescence imaging.
For example, the DiagPlex™ Aldehyde Multiplex PMMA Particles, Dual-color Encoded, 11 µm (Cat. No. DNMM-ADC11) consist of two fluorescent dyes with different fluorescence intensities, allowing the simultaneous detection of up to 9 analytes in a single sample. Up to 100 populations can be defined by combining fluorescence encoding and different particle sizes (11 µm and 15 µm). These aldehyde-containing particles can be individually labeled for antibodies, oligonucleotides and peptides and can be used in standard flow cytometry or fluorescence-based imaging platforms (e.g., fluorescence microscopy systems).
CD Bioparticles’ multiplex fluorescent particles vary in size and fluorescence intensity, allowing researchers to distinguish between different particles and identify the specific analytes to which they bind. For more information about these new particles or multiplex assay development services, please visit https://www.cd-bioparticles.com/products/multiplex-assays-466.html.
About CD Bioparticles
CD Bioparticles is a leading manufacturer and supplier of various nanoparticles, microparticles, and coatings for RD as well as commercialization across different application areas, including in vitro diagnostics, biochemistry, cellular analysis, cell separation, and immunoassay. The company also offers various custom services, including chemical surface-functionalization, fluorescent modification, antibody immobilization, as well as nucleic acid and oligo conjugation to meet client specifications.